Ovulation Cycle Calculator: A Simple Guide To Your Ovulation
Table of Contents
Curious about calculating ovulation and pinpointing your fertile window?
Understanding your ovulation cycle calculator is key to achieving your fertility goals. Ovulation isn’t just a medical term; it’s a critical phase of the menstrual cycle when an egg is released from an ovary. According to the American Pregnancy Association, approximately 1 in 10 women have difficulty getting pregnant or carrying a pregnancy to term because of ovulation disorders.
So, knowing when this happens can make all the difference for those trying to conceive. In this guide, you’ll learn how to track your ovulation, identify the signs, and use simple methods to calculate your most fertile days.
Stay tuned as we break down what you need to know to take control of your reproductive health.
Understanding the Ovulation Cycle Calculator
The ovulation cycle is a natural process that happens in the female body. It’s crucial for understanding your fertility and pinpointing your most fertile days. The cycle consists of three main phases: the follicular phase, ovulation phase, and luteal phase. Each phase plays a key role in preparing the body for a potential pregnancy.
The Follicular Phase
The follicular phase marks the beginning of your menstrual cycle. It starts on the first day of your period and lasts until ovulation. This phase usually spans from 10 to 14 days.
During this phase, the body is busy preparing for ovulation. Here’s what happens:
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): FSH levels rise and stimulate the ovaries to produce many follicles. Each follicle contains an egg.
- Dominant Follicle: Out of all these follicles, only one becomes dominant. This follicle will mature and be ready to release an egg.
- Estrogen Increase: As the follicle grows, it releases estrogen. Higher estrogen levels help thicken the uterine lining to prepare it for a possible pregnancy.
Understanding the follicular phase can help you track your cycle and better estimate when ovulation might occur.
Ovulation Phase
The ovulation phase is the star of the show in your menstrual cycle. Ovulation usually happens around the middle of the cycle and lasts about 24 hours.
Here’s a closer look at this critical phase:
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH) Surge: When estrogen levels peak, it triggers a surge in luteinizing hormone. This LH surge signals the ovary to release the mature egg.
- Egg Release: The mature egg is released from the dominant follicle and travels down the fallopian tube. This is the best time for fertilization.
- Fertile Window: Although the egg only survives for about 24 hours, sperm can survive in the female body for up to 5 days. This creates a fertile window of about 5-7 days where pregnancy is most likely.
Knowing when you ovulate is essential for calculating ovulation and pinpointing your fertile days.

Luteal Phase
The luteal phase follows ovulation and lasts for about 14 days, regardless of your cycle length.
This phase is all about preparing for a possible pregnancy:
- Corpus Luteum Formation: After the egg is released, the follicle transforms into the corpus luteum. This structure releases progesterone.
- Progesterone Role: Progesterone helps maintain the thickened uterine lining, readying it for a fertilized egg to implant.
What happens next depends on whether fertilization occurs:
- If Fertilization Occurs: The fertilized egg implants in the uterine lining, leading to pregnancy. Progesterone continues to support the pregnancy.
- If Fertilization Doesn’t Occur: The corpus luteum breaks down, leading to a drop in progesterone levels. This causes the uterine lining to shed, marking the start of your next period (menstrual phase).
By understanding the luteal phase, you can better recognize the signs of early pregnancy or the onset of your next cycle.
Mastering these phases helps in accurately calculating ovulation and identifying your most fertile days. This knowledge is a powerful tool in taking charge of your reproductive health.
How to Calculate Ovulation
Pinpointing when you ovulate is essential for identifying your most fertile days. There are several methods to help you calculate ovulation with confidence and ease. Here’s a breakdown of the most effective strategies:
Calendar Method
The calendar method is a simple yet useful way to estimate ovulation. The calendar method involves tracking the length of your menstrual cycles to estimate your ovulation date, although this is less reliable than other methods. All you need is a calendar and some patience to track your menstrual cycle over a few months.
- Track Your Period: Mark the first day of your period on the calendar each month. Repeat this for at least three months.
- Calculate Your Cycle Length: Count the number of days from the first day of one period to the first day of the next. This is your cycle length.
- Estimate Ovulation Day: Subtract 14 days from the end of your current cycle. This gives you a rough estimate of your ovulation day. For example, if your cycle is 28 days long, ovulation likely happens around day 14.
While the calendar method is straightforward, it assumes that your cycle is regular. Any variations can affect accuracy.
Basal Body Temperature Method
Your basal body temperature (BBT) is your lowest body temperature in a 24-hour period. Tracking BBT can help you pinpoint ovulation. A study by Dr.Allen Wilcox in the New England Journal of Medicine, found that tracking your BBT can help you identify ovulation with 99% accuracy. To do this, you’ll need to do the following:
- Get a Basal Thermometer: Use a basal thermometer to measure your temperature every morning before getting out of bed.
- Record Your Temperature: Chart your daily readings on a graph or in a fertility app.
- Look for Patterns: Just before ovulation, there will be a slight drop in BBT, followed by a sharp increase. This rise in temperature indicates that ovulation has occurred.
The BabyMad Basal Thermometer for Ovulation is a great option with a 4.3/5 rating!
Easy@Home Digital Basal Thermometer Ovulation with Backlight LCD Display, Premom APP(NOT Bluetooth)
Measures Basal Body Temperature (BBT) to 1/100th of a degree precision (e.g. 36.34℃) in Celsius or Fahrenheit. Use Premom App to track your BBT charting, Cover line and Ovulation test result for your natural family planning journey.
This is an affiliate link
Cervical Mucus Method
Changes in cervical mucus can also help indicate ovulation. When you’re most fertile, your mucus becomes clear, stretchy, and slippery, similar to egg whites. In a study by Dr. Evelyn Billings it was found that women who tracked their cervical mucus were able to identify their fertile window with 97% accuracy.1
- Check Daily: Observe and note the consistency of your cervical mucus daily.
- Look for Changes: Around ovulation, you’ll notice the mucus becomes more abundant, clear, and stretchy.
The kegg® Tech Cervical Mucus Tracker is a revolutionary device on the market that monitors cervical mucus to predict fertility through a fertility tracker, and kegel ball. By using advanced technology, it tracks and analyzes cervical mucus patterns, gives personalized and accurate predictions for ovulation.

A FDA registered medical-grade personalised fertility tracking device in just a couple minutes a day. One time purchase with no additional costs. A 12 months pregnancy guarantee is also included.
This is an affiliate link
Ovulation Predictor Kits
Ovulation Predictor Kits (OPKs) are an effective and convenient way to detect ovulation. They measure levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) in your urine, which surges just before ovulation.
- Follow the Instructions: Each kit comes with specific instructions. Typically, you’ll start testing a few days before your expected ovulation.
- Read the Results: A positive result indicates that you’ll likely ovulate within the next 24 to 48 hours.

Easy@Home 50 Ovulation Test Strips-Width of 5mm
Number 1 ovulation test reader at App Store. Powered by Premom Ovulation Predictor iOS and Android.
This is an affiliate link
Clearblue Advanced Digital Ovulation Tests Kit (OPK), 30 Ovulation Tests
Double Your Chances of Getting Pregnant, with the Clearblue Advanced Digital Ovulation Tests Kit (OPK), 1 Digital Holder and 30 Ovulation Tests
This is an affiliate link
Fertility Devices & Apps
Tech-savvy solutions can also help track ovulation. Fertility apps can help you track your cycle, BBT, and cervical mucus, providing personalized predictions of your fertile window.
Here are some trusted devices that can make the tracking process even easier:

The first and only app to be FDA Cleared and CE Marked. Hormone free and uses your daily temperature readings to predict ovulation.Tracks Luteinizing hormone (LH), Estrogen, follicle-stimulating hormone, progesterone and daily temperature readings.
This is an affiliate link
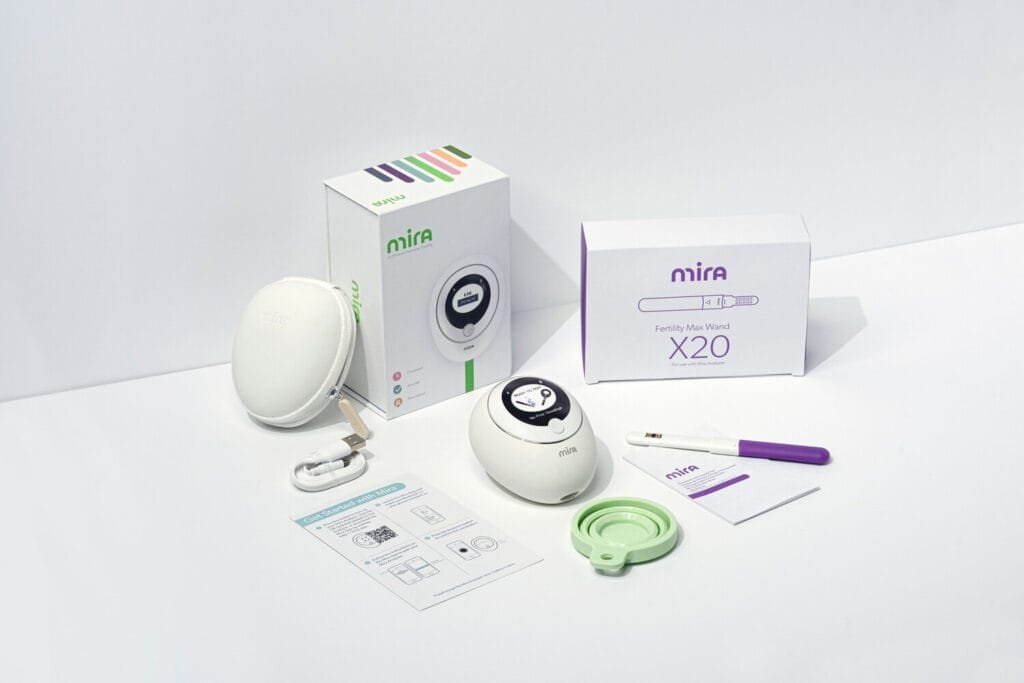

Mira provides real-time data and predictive analytics through analysing hormone levels in your urine to pinpoint your most fertile days. Three kits are available; basic kit, clarity kit, and max kit. Track key fertility hormones (LH, E3G, PdG, and FSH). The kits include wands to predict & confirm your ovulation day and know your 6-day fertile window, and Mira Ovum (FSH).
This is an affiliate link
Using these methods and tools can help you calculate ovulation with greater confidence, making your journey to conception a bit easier.

Accurately calculating ovulation involves a bit of planning and consistency. Each method has its strengths, so consider combining them for the best results.
Factors Affecting Ovulation
Understanding the factors that influence ovulation is essential for anyone trying to conceive. Ovulation can be affected by numerous elements such as stress, lifestyle, health conditions, and diet. By being aware of these factors, you can take steps to ensure a more predictable and healthy ovulation cycle.
Stress and Lifestyle
Stress and lifestyle choices can have a big impact on ovulation. High levels of stress can affect your body’s hormone balance, leading to irregular or missed ovulation. It’s like your body’s way of saying it’s too overwhelmed to focus on fertility at the moment.
- Chronic Stress: High levels of stress over time can disrupt the hormones responsible for ovulation. A study by the University of Louisville found that women who reported high levels of stress had a 29% lower chance of conceiving compared to those with low stress levels.2
- Sleep: Poor sleep patterns also play a role. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
- Exercise: Both too much and too little exercise can affect ovulation. Moderate exercise is key. This is supported by a study that found that women who engaged in high-intensity exercise for more than 60 minutes per day had a higher risk of anovulation (absence of ovulation) compared to those who exercised moderately.3
- Toxic Products: Toxins such as endocrine-disrupting chemicals found in plastics, pesticides, and cosmetics, can also interfere with your reproductive hormones and impact ovulation. Research has found that women with higher levels of bisphenol A (BPA) in their bodies had a higher risk of ovulatory infertility.4 To reduce your exposure to these toxins, choose BPA-free products, opt for organic produce when possible, and avoid storing food in plastic containers.
Simple lifestyle changes can make a big difference in reducing stress and improving your overall well-being, thus helping to regulate your ovulation cycle.

Health Conditions
Certain health conditions can directly affect the ovulation cycle. Conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) are particularly influential.
- PCOS: This condition affects hormone levels, causing irregular ovulation or even the absence of it. Women with PCOS often have lower levels of progesterone, higher levels of androgens and luteinizing hormone (LH), which interfere with ovulation.5
- Thyroid Disorders: Your thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate your body’s metabolism, and when these hormones are out of balance, it can affect your menstrual cycle and ovulation. Both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can disrupt the hormonal balance necessary for regular ovulation. Women with subclinical hypothyroidism may have a higher risk of irregular periods compared to women with normal thyroid function.6
- Obesity: Excess weight can lead to hormonal imbalances caused by insulin resistance and high levels of androgens, both of which can negatively impact ovulation. Research has found that found that women with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher (classified as obese) had a 78% higher risk of irregular menstraul cycle compared to women with a normal BMI. Also, small fat loss of 5-10% could really improve ovulation and fertility in obese women.7
Early diagnosis and treatment of these health conditions can help in managing their effects on your ovulation cycle.
Diet and Nutrition
Diet and nutrition play a crucial role in maintaining a regular ovulation cycle. A balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and nutrients supports overall reproductive health.
- Balanced Diet: Eating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help regulate ovulation, and lower the risk of ovulatory infertility compared to those who follow a diet high in refined carbohydrates and trans fats.8
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is essential for the proper functioning of all bodily systems, including reproductive health.
Key Vitamins and Nutrients:
- Folic Acid: Essential for DNA synthesis and cell growth, helping eggs mature properly.
- Vitamin D: Supports hormone regulation and reproductive health.
- Iron: Important for preventing anemia, which can impact ovulation.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Help regulate hormones and maintain healthy eggs.
- Zinc: Supports cell division and progesterone production.
Including these vitamins and nutrients in your diet can aid in maintaining a consistent ovulation cycle, boosting your fertility, and preparing your body for a potential pregnancy.
Understanding these factors and their impact on ovulation can help you take proactive steps for better reproductive health.
So, Are You Ready To Start Your Ovulation Tracking?
Understanding the ovulation cycle is crucial for anyone trying to conceive. By mastering the phases of the menstrual cycle—follicular, ovulation, and luteal—you can effectively pinpoint your most fertile days.
Calculating ovulation involves using reliable methods such as tracking basal body temperature, observing cervical mucus changes, and utilizing ovulation predictor kits. Combining these strategies can significantly increase accuracy.
Being aware of factors that affect ovulation, like stress, health conditions, and diet, allows you to take proactive steps to maintain a healthy cycle.
Debunking common myths helps clear misconceptions and provides a more accurate understanding of when and how ovulation occurs.
Utilizing this knowledge empowers you to take control of your reproductive health with confidence.
Explore our latest posts:
- 9 Surprising Habits Making Your Period Worse
- Boost Your Fertility with Magnesium: What You Need to Know
- 11 Natural Ways To Balance Your PCOS Symptoms
- How To Improve Your Endometriosis Symptoms: 8 Natural Remedies
- Magnesium’s Impact on the Menstrual Cycle: Boost Your Well-Being
- Billings, E., & Brown, J. B. (1989). The Billings ovulation method: An epidemiological review. The Lancet, 333(8634), 74-76. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(89)91295-8
↩︎ - Louis, G. M. B., Thoma, M. E., Sørensen, D. N., Kim, S., Sundaram, R., & Lynch, C. D. (2011). Stress reduces conception probabilities across the fertile window: Evidence in support of relaxation. Fertility and Sterility, 95(7), 2184-2189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2010.06.078 ↩︎
- De Souza, M. J., et al. (1998). Exercise and reproductive function in women: the role of energy availability. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 83(11), 3361-3365. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.83.11.5241
↩︎ - Ehrlich, S., Williams, P. L., Missmer, S. A., Flaws, J. A., Berry, K. F., Calafat, A. M., & Hauser, R. (2012). Bisphenol A and ovarian dysfunction: Evidence from animal and human studies. Environmental Health Perspectives, 120(5), 647-652. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1104623 ↩︎
- Homburg, R., Armar, N. A., Eshel, A., Adams, J., & Jacobs, H. S. (1988). Influence of serum luteinizing hormone levels on ovulation, conception, and early pregnancy loss in polycystic ovary syndrome. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 66(7), 1046-1048. ↩︎
- Krassas, G. E., Poppe, K., & Glinoer, D. (2010). Thyroid function and human reproductive health. Gynecological Endocrinology, 26(3), 90-98. https://doi.org/10.3109/09513590903472410.
↩︎ - Rich-Edwards, J. W., Goldman, M. B., Willett, W. C., Hunter, D. J., Stampfer, M. J., Colditz, G. A., Manson, J. E., & Hennekens, C. H. (1994). Adolescent body mass index and infertility caused by ovulatory disorder. Human Reproduction, 9(5), 945-950. https://academic.oup.com/humrep/article/9/5/945/608436.
↩︎ - Chavarro, J. E., Rich-Edwards, J. W., Rosner, B. A., & Willett, W. C. (2007). Diet and lifestyle in the prevention of ovulatory disorder infertility. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 86(2), 290-299. ↩︎







One Comment