How To Boost Your Fertility With Antioxidant Foods In 2024
What are Antioxidants? | What Causes Oxidative Stress? | Female Fertility | Male Fertility | How To Reduce Free Radicals | Top Antioxidant Foods
Curious about how your diet can affect your chances of starting a family? The food we consume plays a critical role in reproductive health, as our diets can either hinder or help our fertility. Antioxidant-rich foods, in particular, can boost fertility by combating oxidative stress, which is known to damage sperm and egg cells. This guide explores how antioxidants work, what causes oxidative stress, and which antioxidant-rich foods can support your fertility journey.
What Are Antioxidants?
Antioxidants are natural compounds that act like defenders in the body, neutralizing harmful, unstable molecules called free radicals, also known as reactive oxygen species (ROS). Free radicals are unstable because they seek electrons from other molecules, leading to oxidative stress when there is an imbalance between oxidative stress and the body’s natural antioxidant defenses. This oxidative stress can damage cellular structures such as DNA, proteins, and lipids, resulting in inflammation and cellular damage, including to sperm and eggs, which can reduce fertility.
Antioxidants work by donating electrons to free radicals, stabilizing them and preventing further damage. Some common antioxidants found in everyday foods include vitamin c, vitamin e, beta-carotene, and selenium.
These antioxidants don’t work in isolation but combine their powers to buffer against the damaging effects of oxidative stress, which is a significant factor in impairing fertility. While a small amount of oxidative stress is necessary for some cellular functions, excessive oxidative stress can lead to a negative impact on overall health. Some antioxidants, such as lipoic acid and glutathione, are even produced naturally by the body, but additional antioxidant support through diet can help reduce oxidative stress more effectively.

What Causes Oxidative Stress?
Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body. It can arise from various lifestyle and environmental factors, that directly impacts overall health, including fertility. Understanding these factors can help you make informed choices to minimize free radical production and promote better health.
1. Chronic Stress
Chronic stress can increase free radicals, increasing oxidative stress. This, in turn, disrupts hormonal balance and can interfere with reproductive health—much like how software updates can slow down your phone’s performance.
2. Exposure to Environmental Toxins and Heavy Metals
Heavy metals such as mercury, aluminum, and lead are common environmental toxins that contribute to oxidative stress. Mercury, in particular, is harmful for fertility and accumulates in larger fish like tuna. Opting for smaller fish like sardines, which have lower mercury levels, helps mitigate this risk. Pollution and chemicals in our surroundings similarly add to oxidative stress, akin to how too many apps can bog down a phone.
3. Unhealthy Diet and Food Additives
Processed foods high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and additives can trigger oxidative stress. Fried foods and meals cooked at high temperatures or with reused oils generate free radicals that increase the risk of inflammation and cellular damage. This is much like using low-quality fuel in a high-performance car—it reduces efficiency and harms long-term performance.
4. Sleep Deprivation
Sleep is essential for your body’s repair processes. Skimping on sleep hinders the body’s ability to combat oxidative stress, leaving the door open for cellular damage. Think of sleep as a nightly software update for your brain—it’s vital for keeping everything running smoothly.
5. High-Temperature Cooking
Cooking foods at excessively high temperatures, particularly when they burn, releases free radicals, contributing to oxidative stress. This can have a negative impact on overall health and reproductive function.
How Oxidative Stress Affects Female Fertility?
Oxidative stress acts as a silent enemy, undermining female fertility by contributing to many disorders such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and endometriosis. While a small amount of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is essential for processes like implantation and placental development, unchecked oxidative stress can become destructive, leading to fertility challenges for women. These include:
- Lower Egg Quality and Ovarian Health
Excessive oxidative stress damages egg cells, resulting in poor egg quality and reduced fertility. - PCOS and Insulin Resistance
Women with PCOS often experience insulin resistance, which increases oxidative stress.1 This affects hormonal balance, further complicating ovulation and reducing egg quality. - Endometriosis and Inflammation
Endometriosis is another condition closely linked to increased oxidative stress levels, which increase inflammation and lead to infertility. 2 This makes conception more challenging for affected women. - Hormonal Imbalance and Inflammation
Oxidative stress also worsens hormonal imbalances in women with conditions like PCOS, where reduced insulin sensitivity affects reproductive function. The Inflammation caused by oxidative stress also worsens symptoms in endometriosis, impacting fertility even further
How Oxidative Stress Affects Male Fertility?
Oxidative stress can shake the foundations of male reproductive health, much like filling a high-performance engine with sand—disrupting sperm function at multiple levels. While a small amount of oxidative stress can actually aid sperm function, an excess of free radicals can severely impair fertility. Let’s take a look on how it’s impacted below.
- Sperm Quality and Motility
Oxidative stress directly affects sperm quality and motility, making it harder for sperm to reach and fertilize the egg. 3 - Sperm DNA Damage
Free radicals can fragment the DNA in sperm, leading to genetic abnormalities in embryos and reducing the likelihood of successful fertilization. This DNA damage can result in reduced fertility and may also impact the health of future offspring.4 - Reduced Sperm Production
Oxidative stress interferes with hormone regulation, reducing the levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and testosterone, both of which are crucial for sperm production. Also a high number of reactive oxygen species can disrupt the hormonal feedback loop between the brain and reproductive organs, leading to a lower sperm count. This is particularly evident in men exposed to chronic stress or environmental toxins. - Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Semen Composition
Oxidative stress damages semen composition, including the proteins essential for maintaining sperm health. As a result, both sperm structure and the seminal fluid may suffer, further impacting male fertility.
Oxidative stress negatively impacts multiple aspects of male and fertility, from sperm motility and DNA integrity to hormone regulation and egg quality. Managing oxidative stress through lifestyle changes can help preserve sperm function and overall reproductive health. Let’s take a look at how you can reduce free radicals and in turn oxidative stress in your everyday life!
How To Reduce Free Radicals?
Addressing oxidative stress might sound like a daunting task, but it can be as simple as making small, impactful lifestyle changes. You can fight oxidative stress with some powerful tweaks:
1. Balanced Diet
Load up on colorful fruits and vegetables full of antioxidants. They act like security guards neutralizing the troublemaking free radicals before they can cause any harm.
2. Adequate Sleep
Prioritize good sleep hygiene for at least 7-9 hours each night. Sleep is like rebooting your computer, giving your body a fresh start every day.
2. Exercise Moderately
Regular physical activity helps, but don’t overdo it. Too much exercise can actually increase oxidative stress instead of reducing it. Aim for that sweet spot, like updating your apps just enough to keep them running smoothly.
3. Stay Hydrated
Drink plenty of water to help flush away toxins. Think of water as a smooth-flowing internet connection—speeding up the detox process so everything functions with ease.
3. Use Sunscreen
Protect your skin from harmful UV rays with sunscreen. Consider it your body’s firewall against unexpected sun-induced oxidative stress.
4. Reduce Alcohol and Sugar
Cut back on alcohol and sugary foods, which can accelerate the production of free radicals.
5. Manage Your Weight
Being overweight or underweight can disrupt hormonal balance and increase oxidative stress. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular exercise is important for optimal reproductive health.
6. Reduce Environmental Toxins
Filtering water and minimizing exposure to plastic by opting for glass or stainless steel containers can reduce the intake of toxins that contribute to oxidative stress. Additionally, reducing the consumption of processed foods can minimize exposure to additives and preservatives.
7. Practice Gentle Cooking
Opt for cooking methods like steaming or baking at lower temperatures, as these techniques preserve nutrient content while minimizing the production of harmful free radicals. Avoid burning food, which can increase the risk of carcinogen formation.
Implementing these steps can significantly cut down your oxidative stress levels. Think of them as software updates for your body’s operating system—keeping things running efficiently and smoothly.
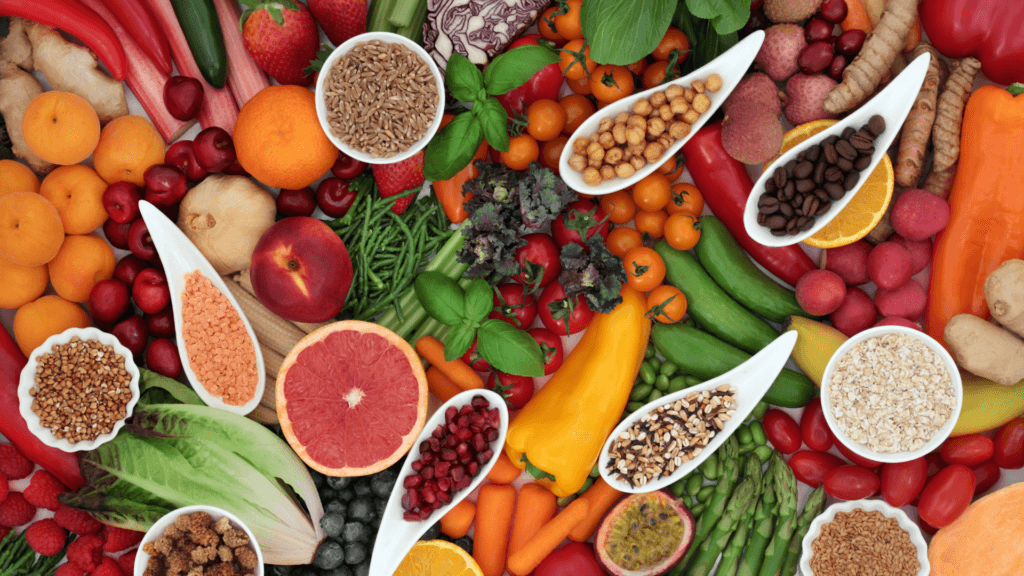
Top Antioxidant Foods To Add Into Your Diet
To boost fertility naturally, adding antioxidant-rich foods to your diet can be highly effective. Here’s a breakdown of some of the top antioxidants and where to find them:
Fruits and Vegetables High in Antioxidants
Fruits and vegetables are packed with antioxidants, including vitamins C and E, carotenoids, and polyphenols. These heavy hitters play a crucial role in boosting fertility by keeping cells healthy.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are rich in flavonoids and vitamins.
- Citrus: Oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are full of vitamin C.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach and kale serve up a healthy dose of carotenoids.
- Bright Vegetables: Carrots and sweet potatoes bring beta-carotene, major players in the antioxidant arena.
Whole Grains and Protein Sources

Don’t overlook whole grains and protein sources when incorporating antioxidants into your diet. Whole grains and protein contribute to a balanced diet, keeping you and your reproductive system in tip-top shape.
- Whole Grains: Quinoa, black rice and brown rice contain selenium and zinc.
- Legumes: Beans and lentils pack protein along with antioxidants.
- Lean Protein: Poultry and seafood, like mackerel and salmon, offer omega-3s that play a supportive role in reducing oxidative stress.
Nuts, Seeds, and Healthy Fats

Nuts, seeds, and healthy fats can be likened to the sturdy foundation of a house, ensuring your health is built on solid ground. They not only taste great but also provide a substantial antioxidant boost.
- Nuts: Almonds and walnuts are sources of vitamin E.
- Seeds: Flaxseeds and chia seeds pump up your routine with omega-3 fatty acids.
- Healthy Fats: Olive oil brings polyphenols, along with heart-healthy benefits.
Beverages Rich in Antioxidants
Why not wet your whistle with beverages loaded with antioxidants? Sipping on the right drinks can also support your efforts to boost fertility.

- Green Tea: An excellent source of catechins, a type of polyphenol known for powerful antioxidant effects.
- Coffee: Offers polyphenols, but remember moderation is key.
- Juices: Opt for 100% fruit juices like pomegranate and acai for their natural antioxidants.
Choosing these foods and beverages empowers you to take control of your fertility in a natural way. In sum, these antioxidant-packed options can be viewed as integral as sunshine is to a budding plant. Implement them into your diet and let that fertility flower thrive!
Summary Of What To Remember
So are you ready to incorporate more antioxidants into your diet?
Antioxidants are essential for ensuring a healthy reproductive system as they are the little warriors that keep oxidative stress at bay, therefore reducing inflammation and cellular damage. Keeping inflammation low is critical for helping you to conceive. So remember the key takeaway for improving your fertility:
Free radicals → High oxidative stress → Inflammation and cellular damage
Antioxidants → Reduced oxidative stress → Improved fertility
Read more of our posts here:
- Seed Cycling: A Natural Approach to Hormonal Balance
- The Best Traditional Chinese Medicine For Fertility
- 11 Ways I Reduced My Period Pain with Natural Remedies
- 9 Surprising Habits Making Your Period Worse
- Boost Your Fertility with Magnesium: What You Need to Know
- Hilali, N., Vural, M., Camuzcuoglu, H., Camuzcuoglu, A., & Aksoy, N. (2020). Increased prolidase activity and oxidative stress in PCOS. Fertility and Sterility, 79(1), 105-110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2003.10.004 ↩︎
- Cacciottola, L., Donnez, J., & Dolmans, M.-M. (2021). Can endometriosis-related oxidative stress pave the way for new treatment targets? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(13), 7138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22137138 ↩︎
- Agarwal, A., Baskaran, S., Parekh, N., Cho, C. L., Henkel, R., Vij, S., & Sharma, R. (2018). Male infertility. Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics, 35(5), 627-646. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-018-1146-6 ↩︎
- Agarwal, A., Bui, A. D., Sharma, R., & Du Plessis, S. (2020). Oxidative stress and its association with male infertility: A clinical perspective. Andrology, 8(4), 832–844. https://doi.org/10.1111/andr.12859 ↩︎







