What You Need to Know About Weight and Male Fertility
The Impact of Weight | Lifestyle Changes to Improve Fertility | Medical Interventions | Psychological Impact
Weight and Male Fertility is becoming a global health crisis, and it’s not just about appearance or heart health. The issue reaches into the intimate sphere of male fertility, a topic that’s gaining serious attention.
This post dives into how obesity affects male reproductive health and what can be done to mitigate these effects. Discover what science reveals about this emerging concern and how you can take steps to improve fertility despite weight challenges.
How Does Weight Affect Male Fertility?
Being overweight can have serious effects on male fertility. Understanding how excess weight influences reproductive health is important for couples trying to conceive.
Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal changes are one major way obesity affects male fertility. Obesity can decrease testosterone levels and increase estrogen levels. Testosterone is the primary male hormone responsible for sperm production. When testosterone levels drop, sperm count and quality can diminish. On the other hand, higher estrogen levels, common in obese men, can further imbalance the body’s hormone levels, reducing overall fertility.
- Testosterone Reduction: Excess fat tissue increases the enzyme aromatase, which converts testosterone to estrogen. This reduces the amount of available testosterone for sperm production.
- Increased Estrogen: Higher estrogen levels can impair the feedback loop that regulates testosterone production, leading to even lower testosterone levels.
The combined effect of these hormonal imbalances can make it difficult for obese men to produce healthy, viable sperm.
Research supports this, with studies showing a direct link between obesity and reduced sperm quality.1Another study highlights how changes in reproductive hormones due to obesity can damage sperm DNA, adding another layer of complexity of fertility issues in obese males.2

Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress associated with obesity also harm male fertility. Inflammation is the body’s response to excess fat and can lead to numerous problems in the reproductive system. So, what exactly is inflammation, and oxidative stress? Let’s take a closer look below.
- Chronic Inflammation: Obesity causes a state of chronic inflammation, where the body’s immune response is always active. This can damage sperm by creating a hostile environment for their development and function.
- Oxidative Stress: Obesity increases oxidative stress, which involves harmful molecules called free radicals. These molecules can damage the DNA in sperm, leading to lower fertility rates.
Imagine oxidative stress as rusting on a car; over time, the damage becomes more severe and affects the car’s performance. Similarly, oxidative stress deteriorates sperm quality, affecting their ability to fertilize an egg.
Understanding these processes is crucial for anyone looking to manage their weight to improve fertility. Recognizing the impact of hormonal imbalance, chronic inflammation, and oxidative stress helps shed light on why obesity-related infertility is such a significant issue.
Reduces Sperm Quality
Obese men are more likely to have a higher proportion of sperm with poor structure. Think of sperm as little swimmers; if they aren’t built right or can’t move well, they won’t reach their goal.
One notable study focused on how obesity affects sperm quality, including motility, morphology, and count. The researchers combined data from 14 different studies, examining differences between overweight, obese, and normal-weight men. They found that excess weight was associated with lower sperm counts, decreased motility, and abnormal morphology.3
This study highlights how obesity can lead to challenges in fertilization and emphasizes the importance of maintaining a healthy weight for reproductive health.
For more information on the findings, you can read about the impact of obesity on sperm function and fertility in detail.
Lowers Testosterone Levels
Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, plays a significant role in sperm production and overall fertility. Research indicates that obese men tend to have lower testosterone levels compared to those of normal weight.
A study revealed that increased weight in men is linked with lower testosterone levels, which subsequently affects sperm quality and fertility. Essentially, when we gain excess weight, our body produces more of an enzyme called aromatase. This enzyme converts testosterone into estrogen, reducing the available testosterone for sperm production.
Here are some significant implications of lower testosterone levels in obese men:
- Reduced Sperm Production: Lower testosterone levels can lead to fewer sperm being produced.
- Decreased Libido: A drop in testosterone often results in a reduced sex drive, further complicating efforts to conceive.
- Hormonal Imbalance: As testosterone decreases and estrogen levels increase, the hormonal imbalance can disrupt the overall reproductive system.
It’s crucial to understand how managing weight can help maintain healthy testosterone levels, thereby improving fertility.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Fertility
Making lifestyle changes can significantly impact fertility, particularly for men who are dealing with obesity. These modifications focus on improving overall health, which in turn, enhances reproductive health. Below are some key areas where lifestyle changes can make a difference.
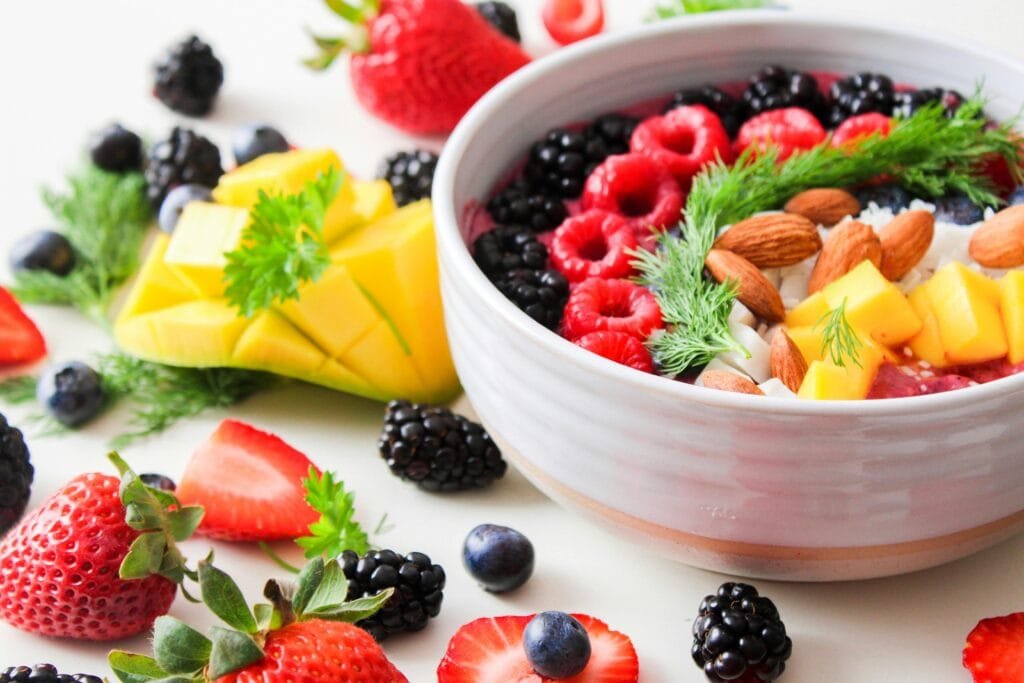
Diet and Nutrition
What you eat plays a vital role in reducing obesity and improving fertility. A balanced diet helps maintain a healthy weight and provides essential nutrients for sperm production and overall reproductive health.4
- Include Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Antioxidants can protect sperm from damage. Foods like blueberries, nuts, and spinach are high in antioxidants.
- Emphasize Lean Proteins: Lean meats, fish, and plant-based proteins can support healthy sperm production.
- Avoid Processed Foods: Processed foods often contain unhealthy fats and sugars, which can contribute to weight gain and poor sperm quality.
- Consume Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish and flaxseeds, omega-3s are crucial for sperm health.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is essential for overall health and can improve blood flow, including to the reproductive organs.

Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise is another crucial component for maintaining a healthy weight and enhancing fertility. Physical activity helps to balance hormones and improve overall health, making it easier to conceive.
- Cardiovascular Exercise: Activities like running, swimming, and cycling can help burn calories and reduce fat.
- Strength Training: Building muscle mass through weightlifting can boost metabolism and improve overall body composition.
- Flexibility and Stress Reduction: Incorporating yoga or pilates can reduce stress and improve flexibility, both beneficial for fertility.
- Consistency is Key: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
The benefits of exercise extend beyond weight loss. Physical activity can lead to a better hormonal balance, reduced stress levels, and increased overall energy—all contributing to improved fertility.
Making these lifestyle changes requires dedication, but the benefits to fertility and overall health make it well worth the effort. Understanding the impact of diet and exercise can empower you to take control of your reproductive health, paving the way for a healthier, more fertile future.
 Photo by Julia Larson
Photo by Julia Larson
Medical Interventions for Obesity and Fertility
While lifestyle changes like diet and exercise can significantly improve fertility, sometimes they aren’t enough. Let’s explore medical interventions that can help men struggling with obesity and fertility issues.
Pharmacological Treatments
Prescription medications can be an effective option for managing obesity. These medications might be prescribed if lifestyle changes alone don’t help you lose weight. These drugs work in various ways, such as reducing appetite or increasing feelings of fullness.
- Appetite Suppressants: Medications like phentermine can help reduce hunger, making it easier to follow a low-calorie diet.
- Fat Absorption Inhibitors: Orlistat prevents the absorption of fat from your diet, which can help reduce calorie intake.
But remember, these should always be used under the supervision of a healthcare provider.
Bariatric Surgery
For men with severe obesity, bariatric surgery might be an option. This surgery significantly reduces the size of the stomach, leading to dramatic weight loss. Different types of bariatric surgery include:
- Gastric Bypass: Creates a small pouch from the stomach and connects it directly to the small intestine.
- Sleeve Gastrectomy: Removes a large portion of the stomach, leaving a tube-like structure.
- Adjustable Gastric Band: Places an inflatable band around the upper part of the stomach to create a small pouch.
Bariatric surgery not only aids in weight loss but can also improve fertility by normalizing hormone levels and reducing inflammation. Read more about the potential benefits and risks in this comprehensive guide on bariatric surgery and fertility.
Hormone Therapy
Given that obesity can lead to hormonal imbalances, hormone therapy might also be beneficial. For men, this typically involves:
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT): Used to restore normal testosterone levels. TRT can improve sperm production and quality, as well as overall energy levels and libido.
But be mindful: TRT should be closely monitored by a healthcare professional, as it can have side effects. For further insights, check out this article on hormonal treatments for obesity-related infertility.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
If medical and surgical interventions don’t suffice, assisted reproductive technologies may be an option. These technologies include:
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): Sperm is directly inserted into the uterus.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): Eggs are fertilized with sperm in a lab and then placed in the uterus.
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): A single sperm is injected directly into an egg.
These methods can help couples struggling with obesity-related fertility issues conceive. For more information, you can visit our articles on IVF and IUI.
By learning about these medical interventions you can better navigate your options for improving fertility. Always consult with healthcare providers to choose the best treatment plan for individual circumstances.

Psychological Impact of Obesity and Male Fertility
The relationship between obesity and male fertility isn’t just physical— it also involves significant psychological elements. Struggling with both obesity and fertility issues can lead to stress, depression, and anxiety, impacting mental well-being and overall quality of life. Understanding these psychological aspects is crucial for men facing this dual challenge.
Mental Health Support
Mental health is an important part of the journey for men dealing with obesity and fertility challenges. Seeking support and implementing strategies can help ease the psychological burden.5
- Counseling and Therapy: Speaking to a mental health professional can provide a safe space to discuss feelings and concerns. Therapists can help develop coping strategies to manage stress and anxiety linked to infertility.
- Support Groups: Joining a support group allows men to share experiences and advice in a communal setting. These groups can also provide a sense of belonging, reducing feelings of isolation.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness and meditation can reduce stress and improve mental clarity. Techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery can be effective.
- Healthy Habits: Incorporating regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep can boost mental and physical health. These habits also positively impact fertility by improving overall well-being.
- Open Communication: Keeping open lines of communication with partners, family, or friends can provide essential emotional support. Being able to talk openly about struggles can be incredibly soothing and reassuring.
Taking care of mental health is as crucial as addressing physical health in overcoming obesity-related fertility issues. By seeking support and employing effective strategies, men can better navigate the emotional complexities of their fertility journey.
To Wrap Up…
Addressing obesity is crucial for improving male fertility. Excess weight can lead to hormonal imbalances, inflammation, and oxidative stress, all of which impair sperm quality and reproductive health. Research highlights how weight reduction through lifestyle changes, medical interventions, or a combination of both can enhance fertility outcomes.
Men should take proactive steps by adopting healthier diets, engaging in regular physical activity, and seeking medical advice when necessary. Understanding these connections empowers individuals to make informed decisions that can positively impact their fertility and overall health.
For those facing these challenges, taking action today can pave the way for a healthier, more fertile future.
Explore our latest posts:
- Seed Cycling: A Natural Approach to Hormonal Balance
- The Best Traditional Chinese Medicine For Fertility
- 11 Ways I Reduced My Period Pain with Natural Remedies
- 9 Surprising Habits Making Your Period Worse
- Boost Your Fertility with Magnesium: What You Need to Know
- Boston, 677 H. A., & Ma 02115 +1495‑1000. (2012, March 15). Excess weight may affect sperm production, reduce fertility in men. News. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/hsph-in-the-news/excess-weight-sperm-fertility/
↩︎ - Katib A. (2015). Mechanisms linking obesity to male infertility. Central European journal of urology, 68(1), 79–85. https://doi.org/10.5173/ceju.2015.01.435 ↩︎
- Palmer, N. O., Bakos, H. W., Fullston, T., & Lane, M. (2012). Impact of obesity on male fertility, sperm function and molecular composition. Spermatogenesis, 2(4), 253–263. https://doi.org/10.4161/spmg.21362 ↩︎
- Sharma, R., Biedenharn, K. R., Fedor, J. M., & Agarwal, A. (2013). Lifestyle factors and reproductive health: taking control of your fertility. Reproductive biology and endocrinology : RB&E, 11, 66. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7827-11-66 ↩︎
- Joja, O.D., Dinu, D.D., & Păun, D. (2015). Psychological Aspects of Male Infertility. An Overview. Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences, 187, 359-363. ↩︎







